www.wimb.net - Slo-Syn - Preset Indexers
Slo-Syn
Museum

Slo-Syn Drives
1977 to 1987
Translators
STM101
ST101
STM103
ST103
TBM105
ST105
BUF105
SB105
TM600
TC600
PDD006
MPS1000
MPS3000
Indexers
PIM151
SP151
PIM153
SP153A
TBM155
SP155A
IM600
IK600
Packaged Preset Indexers
Packaged SLO-SYN motor controls include translators, buffered translators and preset indexers and offer stepping rates of 1000, 3000 and 5000 steps per second. The units are mounted in cabinets for bench or shelf use and can also be mounted in a standard 19" rack. Translators accept pulses from an external source and drive SLO-SYN motors one step for each pulse received. Buffered translators will accept pulses from a fixed, high rate or a random rate source and automatically ramp the pulse rate to accelerate and decelerate the motor. Preset indexers are complete units which provide full control of direction, step rate and distance without external logic.
SP151 and SP151X Packaged Preset Indexers

The SP151 and SP151X SLO-SYN Preset Indexers are enclosed, self-contained units incorporating the power supply and logic circuits needed for precise control of SLO-SYN Stepping Motors in indexing and other positioning applications.
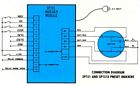
They drive SLO-SYN motors at rates to 1000 steps per second and provide acceleration and deceleration to assure optimum motor control. The SP151 and SP151X can provide indexing motions up to 99,999 motor steps in magnitude, controlled from switches on the front panel. Jog and run modes are also provided.
All functions except count selection can be directed from external switches as well as from the indexer front panel. Voltage levels from a computer or microprocessor can also be used to direct these functions.
SP151: 120 volts a-c +/- 10%, 60 hertz, 3 amperes maximum
SP151X: 220/240 volts a-c +10%-15%, 50/60 hertz, 1.5 amperes maximum
SP153A and SP153AX Packaged Preset Indexers

![]() The SP153A and SP153AX are enclosed, selfcontained units which incorporate the power supply and logic circuits needed for precise control of SLOSYN Stepping Motors in indexing and other positioning applications. They drive the motors at rates to 3000 full-steps or 6000 half-steps with adjustable acceleration and deceleration to provide optimum performance with any appropriate combination of motor and load.
The SP153A and SP153AX are enclosed, selfcontained units which incorporate the power supply and logic circuits needed for precise control of SLOSYN Stepping Motors in indexing and other positioning applications. They drive the motors at rates to 3000 full-steps or 6000 half-steps with adjustable acceleration and deceleration to provide optimum performance with any appropriate combination of motor and load.
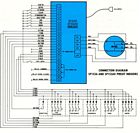
The SP153A and SP153AX can provide indexing counts up to 99,999 motor steps, controlled from the front panel switches, from external BCD logic switches or from a computer or microprocessor. Jog and run modes are also provided. A base speed range of 0 to 1000 full-steps or 0 to 2000 half-steps per second without acceleration or deceleration is incorporated. The motor step increment is 0.90 in the half-step mode and 1.80 in the full-step mode.
Relay contact closures allow the operation of external equipment to be synchronized with the preset indexer.
SP153A: 120 volts a-c +/-10%, 60 hertz, 5 amperes max.
SP153AX: 220/240 volts a-c +10% -15%, 50/60 hertz, 3 amperes max.
SP155A Packaged Preset Indexer

The SP155A is a cabinet mounted motor control containing the power, sequencing and logic circuits needed for bidirectional control of positioning and indexing using a SLO-SYN Stepping Motor. It drives the motor at rates to 5000 full-steps or 10,000 half-steps per second with adjustable acceleration and deceleration. The acceleration is adjustable within a 100 milliseconds to 1 second range and deceleration within a 100 to 500 millisecond range minimum.
The SP155A can provide indexing motions up to 99,999 motor steps, controlled from the front panel, from an external set of BCD logic switches or by voltage levels from a computer or microprocessor. When an index command is given, the indexer will accelerate the motor to the desired rate and continue to step the motor until a specific number of steps remains of the preselected count. At this point the indexer will decelerate the motor, stopping it of the selected position.
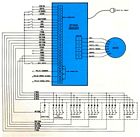
The motor step increment is 0.90 in the half-step mode and 1.80 in the full-step mode. A base speed range provides a low speed of 0 to 1000 full-steps or 0 to 2000 half-steps per second with no acceleration or deceleration. In the high speed range acceleration and deceleration are provided and speed can be adjusted between 200 to 5000 full-steps or 400 to 10,000 half-steps per second.
The SP155A model is adjusted at the factory for compatibility with a specific motor model. The appropriate TBM105 translator/motor combinations are shown in the table.
Updated 2007 Oct. 09


